- Overview
- Recommended Products
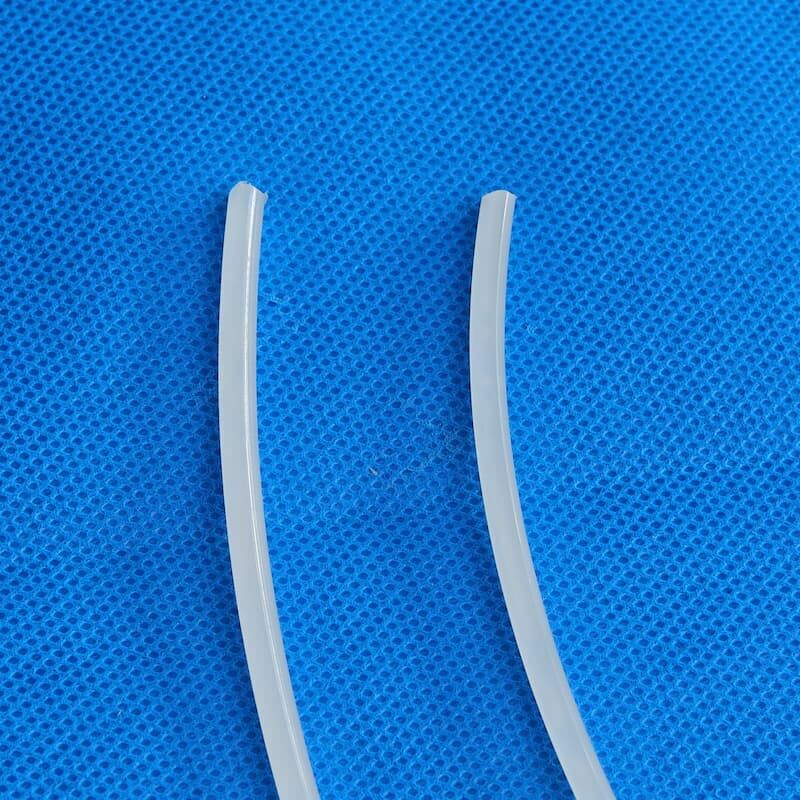
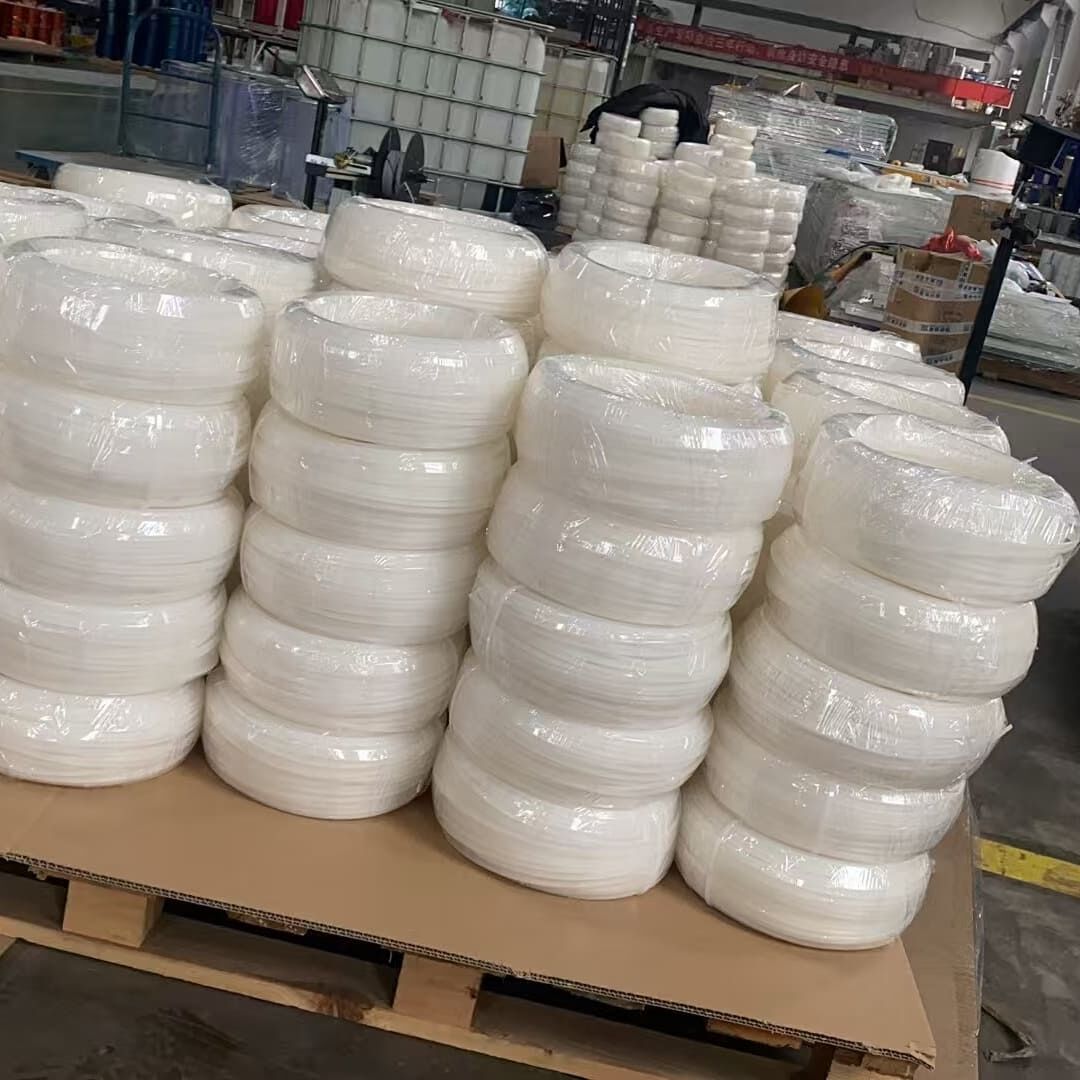
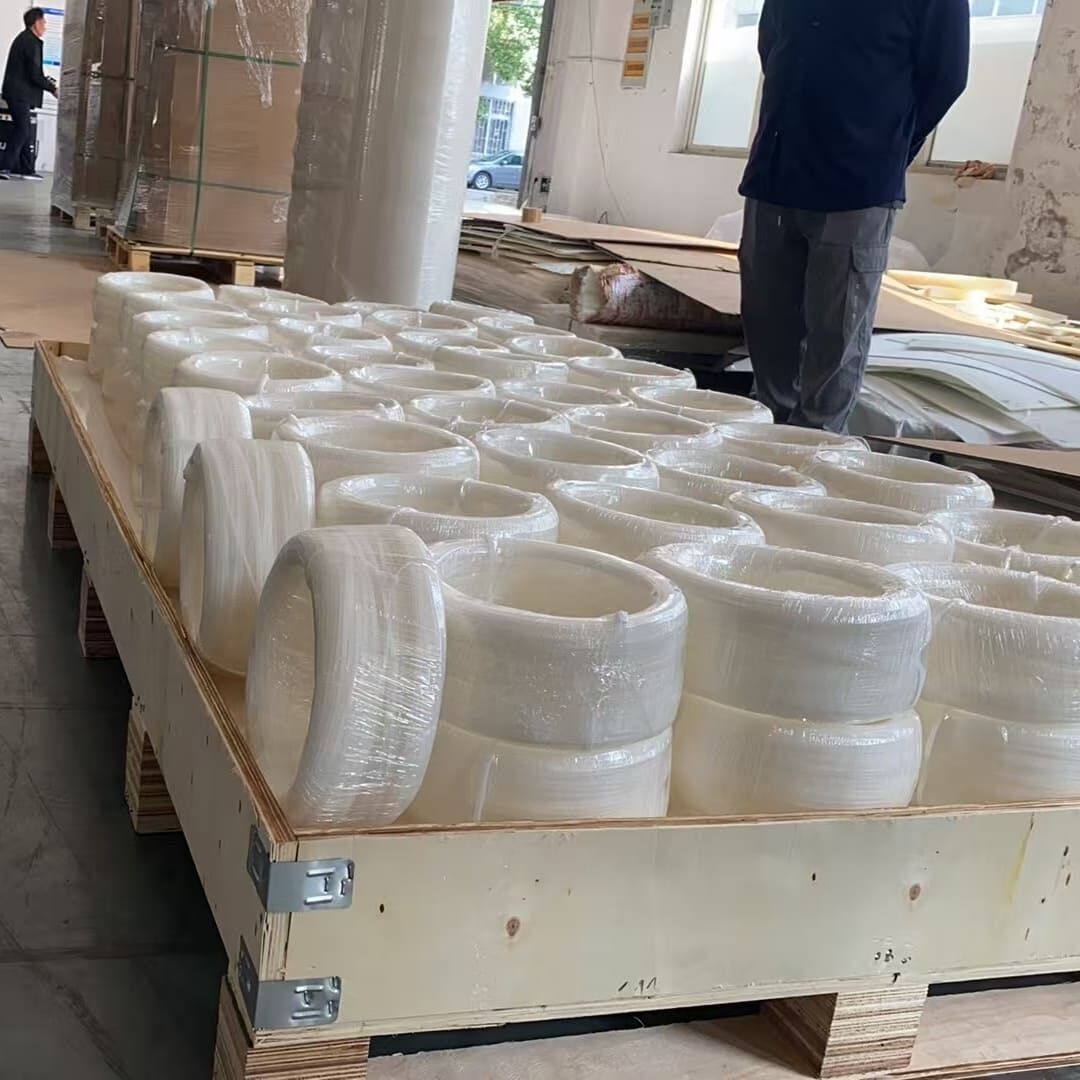
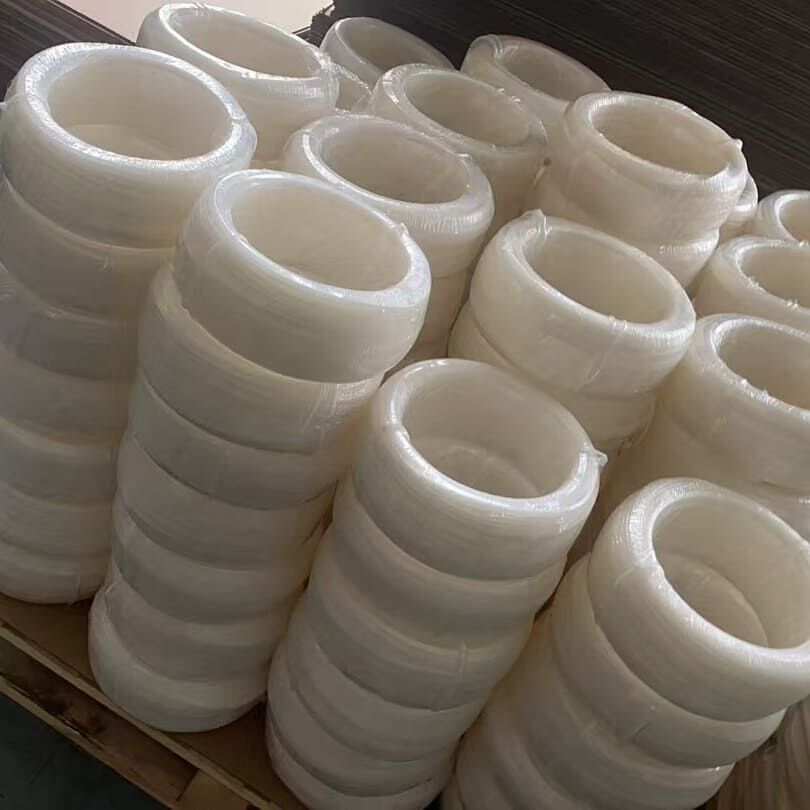
PVDF welding rods are welding materials made of polyvinylidene fluoride plastic. They have a shape similar to slender plastic strips. They are melted by a hot air gun and used as a "adhesive" to connect PVDF pipes or plates. After cooling, the weld formed has similar strength to the base material and high chemical corrosion resistance, and are widely used in the equipment manufacturing and installation of industries such as chemical engineering and semiconductors. Their shape is usually a circular long strip with a diameter of 3-4 millimeters, similar to metal welding rods, hence the name. Its main function is to firmly connect two PVDF components (such as plates, pipes, fittings) together by heating and melting, forming a seamless and integrated structure.
 |
 |
 |
| Item | Value | Unit |
| Density | 1.78 | g/cm |
| Water absorption | <0.4 | % |
| Crystal melting point | 171 | ℃ |
| Embrittlement temperature | <-61 | ℃ |
| Specific heat capacity | 1170 | J/JK·K |
| Linear expansion coefficient | 80*10 | K |
| Heat distortion temperature | 150 | ℃ |
| Decomposition temperature | 316 | ℃ |
| Operating temperature | -40 - 150 | ℃ |
| Pull strength | 49.2 | MPa |
| Elongation | 30-400 | % |
| Compressive strength | 70 | MPa |
| Impact strength | 1.47*10(4) | KI/M2 |
| Hardness | 7 | HB |
| Friction coefficient (to steel) | 0.14 | / |
| Dielectric coefficient (60hz) | 8.4 | / |
| Electrical loss (60hz) | 0.05 | / |
| Volume resistance | 2*10 | Ω/cm |
| Breakdown strength | 10 | Kv/m |
| Arc resistance | 50-70 | S |
| Flammability | self-extinguishing | / |
| Chemical resistance | good | / |
Chemical industry: Corrosion-resistant storage tanks, electrolytic cells, ventilation ducts, spray towers, chemical transportation pipelines.
Semiconductor industry: Ultra-pure water delivery system.
Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology: High-purity water systems, process pipelines.
Electroplating industry: Acid washing tanks, wastewater treatment equipment.
Food industry: Certain situations that meet food-grade requirements.Food industry: Certain situations that meet food-grade requirements.
·High purity
·Excellent resistance to chemical corrosion
·Resistant to high temperatures
·Excellent anti-aging and anti-ultraviolet properties
·Good resistance to wear.
·High strength, high rigidity and excellent creep resistance.
1. What is PVDF welding rod?
It is a plastic welding filler material made of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), used in hot air welding or extrusion welding processes to connect PVDF sheets, pipes and other components.
2. What is its main application?
It is mainly used for manufacturing and repairing equipment that requires extremely high resistance to chemical corrosion, such as chemical storage tanks, electroplating tanks, ultra-pure water delivery pipelines, ventilation systems, etc.
3. What is the basic principle of PVDF welding?
By using high-temperature hot air to simultaneously heat the welding rod and the welding area of the base material, the surfaces of both are melted. They then fuse under pressure and solidify after cooling, forming a strong weld seam with the same performance as the base material.
4. What temperature is required for welding PVDF?
The outlet temperature of the hot air gun should typically be controlled between 350°C and 480°C. If the temperature is too low, the fusion will be poor; if it is too high, the material will decompose (carbonize), which will affect the welding quality.
5. What are the specifications of PVDF welding rods?
The most common specifications are round welding rods with diameters of 3.0mm and 4.0mm. They are also available in different colors (common color/white) to suit different base materials.
6. How to store PVDF welding rods?
They should be stored in a sealed manner in a cool, dry, and clean environment, avoiding direct sunlight, dust and moisture contamination to ensure welding quality.
7. What is the most challenging aspect of welding PVDF?
The key factors are temperature control and the skills of the welders. Operators need to rely on their experience to determine the molten state and maintain a stable welding speed and pressure in order to produce high-quality, defect-free welds.
8. What chemicals can the PVDF welds withstand?
Its corrosion resistance is basically the same as that of the PVDF base material. It can withstand most strong acids, strong bases, halogens and organic solvents, but it is not recommended for use with fuming sulfuric acid, concentrated nitric acid and other strong oxidizing acids, as well as some polar solvents.
9. How to identify the quality of PVDF welding rods?
High-quality welding rods should have uniform color, consistent diameter, no bubbles, and no impurities. When purchasing, choose well-known brands and request the supplier to provide material certification (MSDS). Avoid using inferior products made from recycled materials.
10. What are the main methods for PVDF welding?
Hot air manual welding: The most commonly used, flexible, and suitable for various shapes and positions.
Extrusion welding: It is highly efficient and results in stronger welds. It is particularly suitable for heavy-duty welding of thick plates (≥ 6mm).